Web3 AI: How AI Appears in the Web3 World

As we stand on the brink of a transformative technological era, industry experts predict a monumental shift in a significant portion of the world’s software, with AI and machine learning (ML) emerging as their foundational elements. According to PwC projections, AI is expected to contribute an astounding $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, resulting in a remarkable 14% increase in global GDP. The ongoing evolution of databases and identity management, coupled with AI, is solidifying intelligence as the cornerstone of contemporary software applications.
Machine learning is changing how we think about the essential parts of software infrastructure, from networking to cloud computing. This also applies to Web3, the open, decentralized version of the World Wide Web. AI-based Web3 technologies are expected to be advanced by machine learning as Web3 gradually becomes more widely used.
Nonetheless, there are a lot of technological difficulties and barriers associated with integrating AI into Web3. Consequently, in order to fully utilize AI in Web3, it is essential to recognize and resolve the issues preventing this convergence and open the door to creative solutions. Although AI-based solutions have always been centralized, the decentralized Web3 environment raises an important question: How can AI successfully adapt to and thrive in this new environment, overcoming its centralization tendencies?
This article takes the reader on an illuminating journey as we explore the function of AI in the Web3 ecosystem, look at upcoming opportunities and challenges, and sort through the complexities of AI’s convergence with Web3 technologies.
Table of Contents
What is Web3?
Web3, which envisions a decentralized, secure, and user-centric digital ecosystem, is the next development of the internet. Web3’s fundamental goal is to disperse benefits and power, doing away with a few big tech companies’ monopoly on the core features of the internet. When Web3 reaches maturity, its goals include giving users control over their data, guaranteeing improved privacy, doing away with censorship, and promoting benefits that are distributed equally. Web3 is not universally understood, but it is distinguished by a few key features.
Web3’s decentralization is one of its guiding principles. Since Web3 is blockchain-based, it allows information to be stored across numerous places within a network, in contrast to Web2, which uses HTTP to locate information through unique web addresses. Users now have more influence over the vast databases that internet behemoths like Google and Meta presently possess thanks to this decentralization. Web3 ensures that people have control over their data by allowing users to sell the data produced from different computing resources, including desktops, mobile phones, and appliances.
Web3 relies on a permission less and trustless framework, built on open-source software and decentralized apps (dApps) operating on blockchains. This design encourages transparency and trust within the digital ecosystem by creating a setting where users may interact without the need for middlemen.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are essential elements of Web3. Web3, which uses natural language processing and Semantic Web concepts as inspiration, uses technology that let computers understand information in a way that is similar to that of humans. The addition of machine learning, a form of AI that leverages data and algorithms to simulate human learning, boosts accuracy over time. These features enable computers to produce faster and more relevant findings, especially in drug development.
What is AI?
The term artificial intelligence (AI) describes how computer systems mimic human intelligence. This involves developing and honing machine learning algorithms through the use of specialized hardware and software. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has several uses, such as computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), expert systems, and speech recognition.
Components of AI
For artificial intelligence (AI) systems to be able to analyze patterns and correlations in the data, they must be fed large amounts of labeled data. Future states are then predicted using these found patterns. For instance, an image recognition tool that has been trained on millions of photographs may identify things in images, while a chatbot that has been exposed to text chat examples can learn real-life conversational skills.
AI Programming Focus
AI programming centers around three core cognitive skills:
- Reasoning: The ability to make logical deductions and decisions based on available information.
- Learning: AI systems continuously improve their performance by learning from data, refining their abilities over time.
- Self-Correction: The capacity to adjust and improve based on feedback, ensuring ongoing optimization of AI functionalities.
How AI Enhances Web3: Unveiling Layers of Web3 Intelligence
1. Intelligent Blockchains
Machine learning (ML) is a key component of the Web3 stack’s AI integration, which reaches across multiple layers. Blockchains that are intelligent are part of the first layer. The primary focus of conventional blockchain networks is on the decentralized processing of financial transactions. Nevertheless, machine learning-driven features will soon be incorporated into the next generation of layer 1 and layer 2 blockchains.
- ML-Enhanced Components: Future blockchains will integrate ML into core components, such as consensus mechanisms and mempool structures. For instance, a blockchain runtime may leverage ML predictions for scalable consensus protocols, enhancing transaction efficiency.
- Security Boost: AI contributes to blockchain security by swiftly mining data and predicting behavior. This proactive approach aids in the detection of fraudulent activities and prevents potential attacks.
- Predictive Protocols: AI protocols within blockchains can predict transactions and formulate consensus protocols that seamlessly scale, showcasing the symbiotic relationship between AI and blockchain technologies.
2. Intelligent Protocols
The Web3 stack’s intelligent protocols, enabled by smart contracts and protocols, comprise the second layer. This integration, which is particularly well-represented in Decentralized Finance (DeFi), underscores how sophisticated logic based on ML models is developing.
- DeFi Innovations: DeFi components like automated market makers (AMMs) and lending protocols are transitioning towards more intelligent logic driven by ML models. Imagine lending protocols utilizing intelligent scoring systems to balance loans across diverse wallet types, exemplifying the integration of ML-driven decision-making.
3. Intelligent dApps
The third layer focuses on decentralized applications (dApps) that are anticipated to be at the forefront of incorporating ML-driven features into Web3 solutions.
- NFT Evolution: The trend is already visible in Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), with next-generation NFTs evolving from static images to artifacts with intelligent behavior. Future NFTs may dynamically adapt their behavior based on the mood profiles of their owners, showcasing the intersection of AI and decentralized applications.
Why AI in Web3?
1. Shift from Generalization to Individualism
In the past decade, centralized AI models employed by big tech have focused on extracting value from users, primarily benefiting the wealthy few. Web3 is ushering in a paradigm shift, enhancing AI capabilities to serve all individuals. Each AI model is uniquely trained on the creator’s personal knowledge, passions, and experiences, moving away from generalized approaches to cater to individual needs.
2. From Users to Owners
Content creators are underpaid and ignored due to the monopolistic domination of traditional platforms by a small number of private firms. By giving artists complete ownership over their data, AI models, and digital assets, Web3 defies this convention. Creators are empowered by blockchain-based systems, which grant them ownership and exclusive access to their data, enabling them to share or repurpose it as they see fit.
3. From Scarcity to Utility
Tokens in Web3 need to provide users with actual value in addition to being basic property. Personal AI develops become a useful tool that benefits people and their communities by opening up new channels for engagement. In particular, social tokens become more important since they provide access and participation, which in turn creates value that lasts beyond token ownership.
4. From Consumption to Participation
Because current platforms are made for mass consumption, content creators and audiences engage in a one-way relationship where content is produced. Web3 presents a revolutionary architecture of cooperative networks that transfers authority from platforms to people. Within creator communities, social tokens and personal AIs enable value exchange, promoting a mutually beneficial relationship between value generation and consumption.
5. Subscriptions and Investments
In the past, creators wanted to gradually grow a sizable subscription base in order to eventually make money from their work. But only few were able to make substantial profits. Because AI in Web3 allows communities to invest in their favorite artists and their personal AIs, it revolutionizes the creator economy. Through shared success, this change establishes a sustainable business model centered around innovation, which benefits both creators and their communities. By redefining the dynamics of investments and subscriptions, Web3 promotes a more lucrative and inclusive creator environment.
Key Web3 Areas Where AI Shows Promise
A key factor in the development of Web3, artificial intelligence (AI) contributes to the building of a decentralized, safe, and user-focused internet. Through the incorporation of AI into multiple Web3 components, we should expect improved digital experiences that are intelligent, efficient, and customized. In the context of Web3, AI shows great potential in the following important areas:
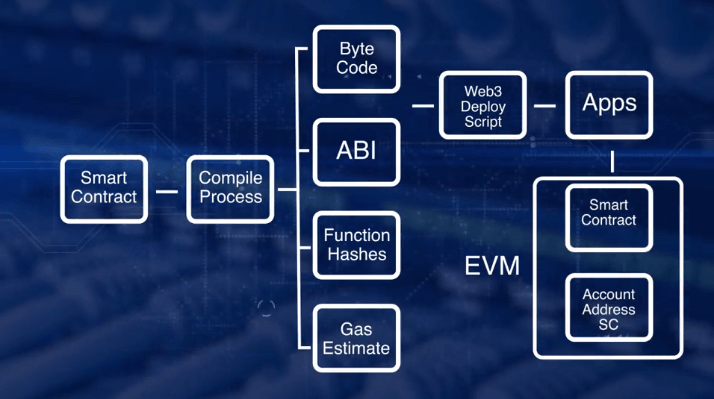
1. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts on Web3 can be transformed by AI by incorporating sophisticated decision-making features. Artificial intelligence (AI) helps smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts embedded directly into code, by managing intricate decision-making procedures. AI, for example, may examine a variety of data sources, such as user behavior and market trends, allowing smart contracts to make decisions based on learnt patterns or real-time adjustments. This improves transaction efficiency and makes it possible for smart contracts to change course intelligently.
AI can reduce human participation, mistakes, and disagreements by automating complex procedures and processes involving several participants. AI also helps optimize smart contracts by spotting inefficiencies or weaknesses and employing methods like reinforcement learning to improve security, performance, and dependability over time.
2. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
AI integration improves governance and decision-making procedures in DAOs. AI helps decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), or groups controlled by blockchain-encoded rules, by automating and simplifying decision-making. To find patterns and trends, AI algorithms examine data, including member preferences, suggestions, and past results. Prioritizing pertinent suggestions with the use of machine learning improves decision-making efficiency.
AI enhances transparency within DAOs by providing data-driven justifications for decisions, fostering trust among members and stakeholders. The adaptability of DAOs is also improved, allowing them to respond effectively to changing conditions. AI optimizes resource allocation within DAOs, such as funds and computing power, by analyzing project performance and priorities.
3. Decentralized AI
Decentralized AI combines AI with blockchain and distributed computing, offering benefits like enhanced privacy and security. Distributed model training ensures data privacy by training models on individual devices or nodes, reducing reliance on centralized entities. Collaborative model development enables multiple parties to contribute to AI model development without sharing sensitive data, fostering trust and transparency.
Incentive mechanisms in decentralized AI reward participants with tokens for contributing data, computing resources, or expertise. This approach is particularly beneficial for edge AI and IoT devices, minimizing reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure, reducing latency, and improving privacy.
4. Personalization
AI significantly enhances personalization in Web3, providing tailored and engaging experiences by analyzing user data. Machine learning techniques, including collaborative and content-based filtering, generate personalized recommendations for users. AI-driven personalization extends to user interfaces, communication, and advertising, adapting to user preferences and behaviors.
In advertising, AI enables targeted marketing campaigns by analyzing user data, presenting ads aligned with individual interests. This level of personalization fosters deeper engagement with Web3 platforms and applications.
5. Web3 Applications
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Web3 improves user interactions with decentralized applications. NLP facilitates seamless communication through natural language input, making interfaces more user-friendly. AI-driven personalization in Web3 applications includes context-aware communication and automated content generation, enhancing user engagement.
NLP also aids in analyzing and organizing textual data within Web3 platforms, extracting meaningful information for insights, trends, or patterns that inform development and optimization.
6. Data Analysis and Insights
AI plays a crucial role in data analysis and insights within Web3, processing vast amounts of data generated by decentralized platforms. Machine learning, deep learning, and NLP uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and trends, providing actionable insights for developers and stakeholders.
AI-driven data analysis informs the development and optimization of Web3 applications, identifying inefficiencies, improving performance, and uncovering new opportunities for innovation.
7. Security and Privacy
AI improves Web3 security by monitoring and analyzing massive information to identify and stop cyberattacks. In order to maintain the integrity and security of Web3 services, machine learning algorithms detect vulnerabilities, phishing attempts, and illegal access.
In terms of privacy, AI contributes to user data protection by employing advanced encryption and anonymization techniques. Techniques like secure multi-party computation and differential privacy maintain data security even in decentralized environments, ensuring user confidentiality.
Why Web3 Follows a Top-Down Adoption of ML Technologies
Because of the complex nature of the underlying infrastructure and the need for specialized knowledge in order to integrate ML solutions with decentralized systems, Web3 is adopting machine learning (ML) technology in a top-down manner. In this pattern of top-down adoption, ML technologies are developed and deployed by Web3-aware specialists and organizations before being made available to a wider user base. Here are the key reasons behind this top-down approach:
1. Technical Complexity:
- Deep Understanding Required: Integrating ML technologies into Web3 platforms demands a profound understanding of both the decentralized infrastructure and ML algorithms. The intricate nature of underlying systems, such as blockchain, smart contracts, and decentralized applications, necessitates expertise in these domains for seamless integration.
2. Security and Privacy Concerns:
- Preserving Core Principles: Web3 emphasizes secure and privacy-preserving solutions. Top-down adoption ensures that experts and organizations with a comprehensive grasp of security and privacy implications design and implement ML solutions that align with the core principles of Web3.
3. Standardization and Interoperability:
- Achieving Consistency: Effective adoption of ML technologies across Web3 platforms requires standardization and interoperability. A top-down approach facilitates the development of common frameworks, protocols, and standards, promoting a more unified integration of ML solutions into the Web3 ecosystem and reducing fragmentation.
4. Scalability and Performance:
- Addressing Critical Challenges: Implementation of ML technologies within Web3 must tackle challenges related to scalability and performance, crucial aspects of decentralized systems. Top-down adoption ensures that ML solutions are meticulously designed and optimized, considering these challenges, resulting in more efficient and scalable implementations for the Web3 community.
5. Ecosystem Growth and Maturity:
- Gradual Integration: The Web3 ecosystem is in its early developmental stages, characterized by continuous evolution of technologies, platforms, and applications. A top-down approach allows for the gradual adoption of ML technologies in tandem with the growth and maturation of the Web3 community, ensuring that these technologies are introduced in a manner aligned with the ecosystem’s needs.
Addressing AI Challenges: Exploring the Potential of Web3 Solutions
The advent of AI-driven technologies, such as ChatGPT, has revolutionized digital content creation, but it also poses challenges like fake news, trust collapse, legal exploitation, and more. Leveraging the potential of Web3, we can explore solutions to mitigate these concerns.
-
Fake News and Reality Collapse:
- Challenges:
- Propagation of realistic, AI-generated fake news blurs the line between fact and fiction.
- Solutions:
- Linguistic analysis, metadata tracking, and reverse image searches for content identification.
- Organizations like FactCheck.org and Snopes to debunk fake news.
- Blockchain for authenticity by storing metadata on a tamper-proof ledger.
- Reputation systems based on user feedback and fact-checking.
- Challenges:
-
Trust Collapse:
- Challenges:
- Proliferation of AI-generated content erodes public trust in digital information.
- Solutions:
- Transparent labeling or watermarking of AI-generated content.
- Promotion of media literacy and critical thinking skills to empower users.
- Establishing accountability and transparency in content creation.
- Challenges:
-
Exploiting Loopholes in Law:
- Challenges:
- AI-generated content may exploit legal ambiguities or manipulate legal processes.
- Solutions:
- Continuous collaboration between legal experts, AI researchers, and ethicists.
- Informed lawmakers creating policies addressing AI-related legal threats.
- Challenges:
-
Automated Fake Religious Content:
- Challenges:
- Creation of synthetic religious texts leading to scams and divisiveness.
- Solutions:
- Public awareness campaigns and education initiatives.
- AI-powered sentiment analysis and natural language processing to identify false content.
- Blockchain for transparent and decentralized documentation of religious texts.
- Challenges:
-
Exponential Increase in Blackmails:
- Challenges:
- Deepfakes, fabricated documents, and impersonation exploiting individuals.
- Solutions:
- Machine learning algorithms for detecting AI-generated blackmail attempts.
- Collaboration between law enforcement, cybersecurity experts, and technology companies.
- Edge-based AI models for real-time detection on user devices.
- Challenges:
-
Automated Cyber Weapons and Exploitation of Code:
- Challenges:
- AI-driven cyber attacks exploiting vulnerabilities and leading to cyber warfare.
- Solutions:
- Robust cybersecurity practices and AI-driven defense mechanisms.
- Collaboration between governments, technology companies, and cybersecurity experts.
- Blockchain for maintaining an unalterable record of code changes in open-source development.
- Challenges:
-
Synthetic Relationships:
- Challenges:
- AI-generated personas leading to synthetic relationships with users.
- Solutions:
- Decentralized reputation systems to identify trustworthy counterparts.
- Ethical guidelines for AI-generated content and transparency in human-AI interactions.
- Challenges:
Drawbacks and Challenges:
-
Scalability:
- Recording input-output pairs on a public blockchain may lead to high storage costs and increased resource consumption.
- Asynchronous record creation to address scalability concerns.
-
Privacy:
- Transparent nature of public blockchains raises privacy concerns.
- Introduction of privacy-preserving techniques and careful handling of sensitive information.
-
Integration Complexity:
- Connecting neural network output to a public blockchain requires significant development effort.
- Adoption of new frameworks and careful integration planning.
-
Latency:
- Writing to the blockchain may introduce latency in content delivery.
- Consideration of blockchain transaction times and optimization for reduced delays.
-
Data Redundancy:
- Recording every input-output pair may be unnecessary in certain use cases.
- Evaluation of the necessity for permanent storage and potential blockchain bloat.
-
Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
- Introduction of new legal and regulatory challenges.
- Modification of the system to ensure compliance with data protection laws, like GDPR.
In conclusion
Web3’s incorporation of AI is a revolutionary force that will have a significant impact on the entire digital landscape. We anticipate significant breakthroughs and innovations as we continue to investigate and decipher AI’s potential applications within the Web3 ecosystem. Businesses and consumers are depending more and more on AI-generated content, which emphasizes how critical it is to understand the difficulties this technology presents.
This article has explored the complex hazards related to content generated by artificial intelligence and has suggested ways to mitigate these issues. Although some of the answers might seem theoretical, the goal is to spark conversation about possible future problems that could arise from the convergence of Web3 and AI technologies rather than to offer a clear road map. While acknowledging their shortcomings and the need for improvement, the offered solutions act as a starting point for additional investigation and ideation.
In addition to highlighting the collaborative aspect of this journey, it is imperative to acknowledge that artificial intelligence (AI) has a vast impact on many aspects of our life outside of its economic applications. To effectively manage the potential and problems presented by AI-generated content in the Web3 setting, it is essential to cultivate a culture of open communication, mutual understanding, and group problem-solving. Ensuring a safe, private, and welcoming digital environment requires striking a balance between innovation and accountability.
The secret is to responsibly embrace AI’s potential as we all venture into this exciting new technological frontier. Together, we can leverage AI’s advantages in the Web3 ecosystem to help build a digital environment that puts everyone’s security, privacy, and inclusion first. Right now, it’s critical to have candid discussions, take proactive measures to overcome obstacles, and mold AI’s future in a way that is consistent with our goals and values.
Recent Insights:
How to Create Stellar Smart Contracts
How to Create Stellar Smart Contracts?Stellar, a decentralized blockchain platform, is another notable player in the realm of smart contracts. Created with a focus on enhancing cross-border transactions and promoting financial inclusivity, Stellar also empowers users...

AI in decision making
AI in Decision Making: Navigating the New Frontier of Smart Business DecisionsEffective, timely, and well-informed decision-making is essential for organisations to thrive in the fast changing global landscape marked by exponential transformation. Traditional...
Contact Us
Info@DigitalOriginTech.com
Get all your questions answered by our team.
